Technology known as artificial intelligence, or AI, makes it possible for computers and other devices to mimic human intelligence and problem-solving skills.
AI is capable of carrying out tasks that would normally require human intelligence or assistance, either on its own or in conjunction with other technologies (such as sensors, geolocation, and robotics). A few instances of AI in the news and in our daily lives are digital assistants, GPS navigation, driverless cars, and generative AI tools (like Open AI’s Chat GPT).
Table of Contents

Artificial intelligence is a branch of computer science that includes machine learning and deep learning and is frequently discussed in conjunction with them. In these fields, artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms that mimic human decision-making processes are developed with the ability to “learn” from available data and produce progressively more accurate classifications or predictions over time.
Despite the various hype cycles surrounding artificial intelligence, even detractors appear to agree that ChatGPT’s release represents a sea change. The previous time, generative AI was this significant; advances in computer vision led the way; this time, natural language processing (NLP) is leading the way. In addition to human language, generative AI has the ability to learn and synthesize many kinds of data, such as photos, videos, software code, and even molecular structures.
The uses of AI are expanding daily. However, as the excitement surrounding the application of AI technologies in business grows, discussions about responsible AI and AI ethics become vitally relevant. To learn more about IBM’s position on these matters, see Building Confidence in AI.
Types of Artificial Intelligence: Weak AI Vs. Strong AI
Artificially narrow intelligence (ANI), also referred to as weak AI, is AI that has been educated and targeted to carry out particular tasks. The majority of the AI that exists today is powered by weak AI. Since this kind of AI powers some highly powerful applications, including Apple’s Siri, Amazon’s Alexa, IBM WatsonxTM, and self-driving cars, “narrow” could be a better description.
Artificial general intelligence (AGI) and artificial super intelligence (ASI) comprise strong AI. General artificial intelligence, or AGI, is a speculative branch of AI in which a machine is endowed with human-level intelligence. This machine would be self-aware, possess consciousness, be able to solve problems, learn, and make future plans. Superintelligence, or ASI, would be more intelligent and capable than the human brain.
Even though there are currently no working examples of strong AI, it remains purely theoretical, but that doesn’t stop academics from studying its advancement. In the interim, science fiction characters like HAL, the superhuman and renegade computer aide from 2001: A Space Odyssey, may provide the best illustrations of ASI.
Deep Learning Vs. Machine Learning
AI comprises the subdisciplines of machine learning and deep learning, with the latter being a subdiscipline of the former.
Neural networks are used by both machine learning and deep learning algorithms to “learn” from massive volumes of data. These neural networks are programming structures inspired by the way the human brain makes decisions. They are made up of layers of networked nodes that combine to extract features from the data and forecast what the data might indicate.
The kinds of neural networks used in machine learning and deep learning, as well as the degree of human intervention required, are different. Neural networks having an input layer, one or more “hidden” layers, and an output layer are used in traditional machine learning techniques. These algorithms are typically restricted to supervised learning, meaning that in order for the algorithm to extract characteristics from the data, the data must first be organized or labeled by human specialists.
Deep neural networks, which consist of an input layer, three or more (often hundreds) hidden layers, and an output structure, are the basis for deep learning techniques. Unsupervised learning is made possible by these several layers because they automate the feature extraction process from sizable, unstructured, and unlabeled data sets. Deep learning basically makes machine learning at scale possible because it doesn’t require human intervention.
Artificial Intelligence Applications
1. Speech Recognition
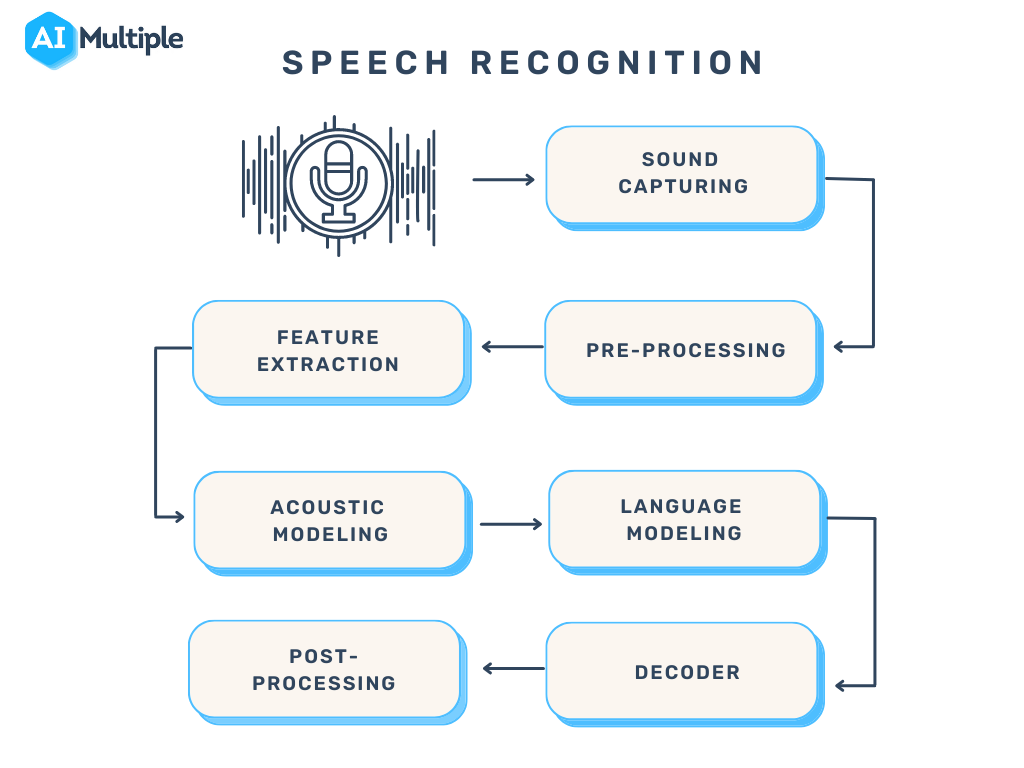
It is a feature that employs natural language processing (NLP) to convert spoken human speech into written form. It is also known as automatic speech recognition (ASR), computer speech recognition, or speech-to-text. Speech recognition is a feature that many mobile devices have built into their systems to enable voice search (like Siri) or increase messaging accessibility.
2. Customer Service

Along the client journey, online virtual agents are taking the place of real representatives. The way we think about customer involvement across websites and social media platforms is being altered by their responses to commonly asked questions (FAQs) concerning subjects like shipping and their personalized advice, which may include cross-selling products or sizing recommendations. Examples include virtual agent-powered messaging bots on e-commerce sites, messaging applications like Facebook Messenger and Slack, and activities often performed by voice assistants and virtual assistants.
3. Computer Vision

Thanks to artificial intelligence (AI) technology, computers and other systems can now interpret digital photos, movies, and other visual inputs to obtain meaningful information. Then, they may act accordingly. It differs from picture recognition tasks in that it can offer recommendations. Convolutional neural networks are the brains of computer vision, which finds uses in social media photo tagging, radiological imaging in healthcare, and autonomous vehicles in the automotive sector.
4. Anomaly Detection

Large datasets can be combed through by AI models, which can then identify unusual data items. These abnormalities may draw attention to defective machinery, mistakes made by people, or security lapses.
In the End
The goal of artificial intelligence (AI), a broad field of computer science, is to create intelligent machines that can carry out tasks that normally call for human intelligence. Even though artificial intelligence (AI) is an interdisciplinary discipline with many different techniques, developments in machine learning and deep learning, in particular, are completely changing almost every industry. We hope to have enlightened you with this article on artificial intelligence. For more such articles, keep tabs on Digital Gabbar.
Also Read: Digital Marketing is Booming: Top 5 Digital Marketing Tips for Your Brand
